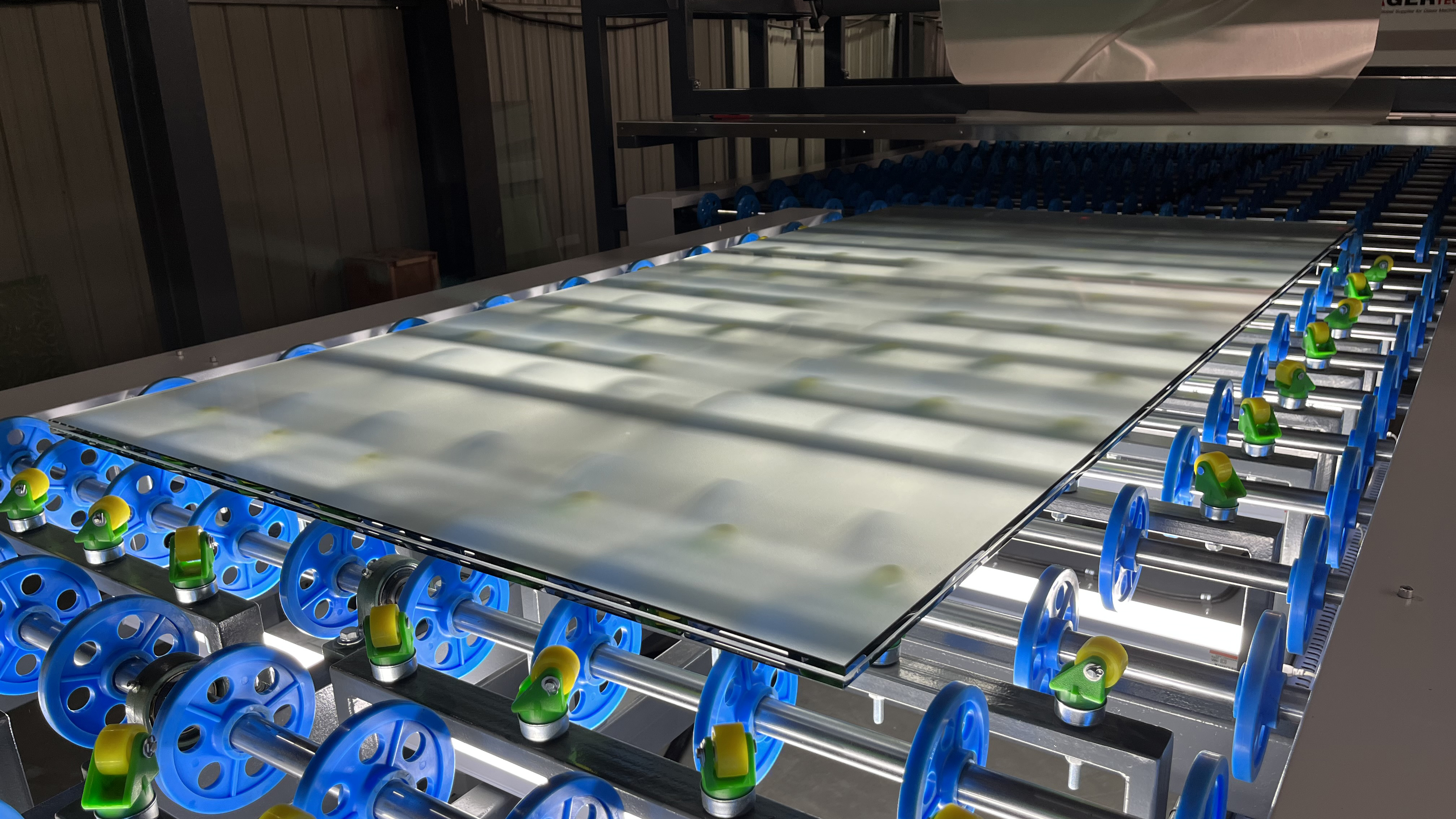
Laminated glass is made by combining two or more layers of annealed or tempered glass with a layer of plastic film. The result is a highly secure window construction that provides superior protection against break-ins and other threats. Laminated glass also meets many code requirement applications, providing significant construction benefits in terms of load deflection criteria and safety. Though there are some drawbacks to using laminated glass such as cost and weight, it can be used to replace annealed or tempered glass when post-construction security is required. Additionally, it offers many advantages in terms of sound reduction and energy efficiency.
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass that is composed of two or more panes of normal annealed glass, which are bonded together with one or more plastic layers. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance compared to normal annealed glass, meaning that it is less likely to shatter and produce sharp shards when impacted. This makes it much safer than ordinary glass as any broken pieces will stick together rather than falling apart and causing serious injuries on rare occasions. When considering the type of safety glass you should use in your home, laminated types are a great option as they greatly reduce the chances of injury due to broken shards.
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass held together with a sturdy interlayer, usually made from lonoplast polymers. This interlayer is usually a thermoplastic resin such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), and the two sheets are united together with the help of a liquid resin such as polyurethane tpu or vinyl acetate. The two sheets are sealed together by applying heat and pressure, creating an inseparable bond between them. The plastic interlayers ensure that if the glass is broken, it will remain in one piece due to the pressure created by the resin. Laminated safety glass is much more secure than other types due to its ability to withstand greater force even in the event of breakage.
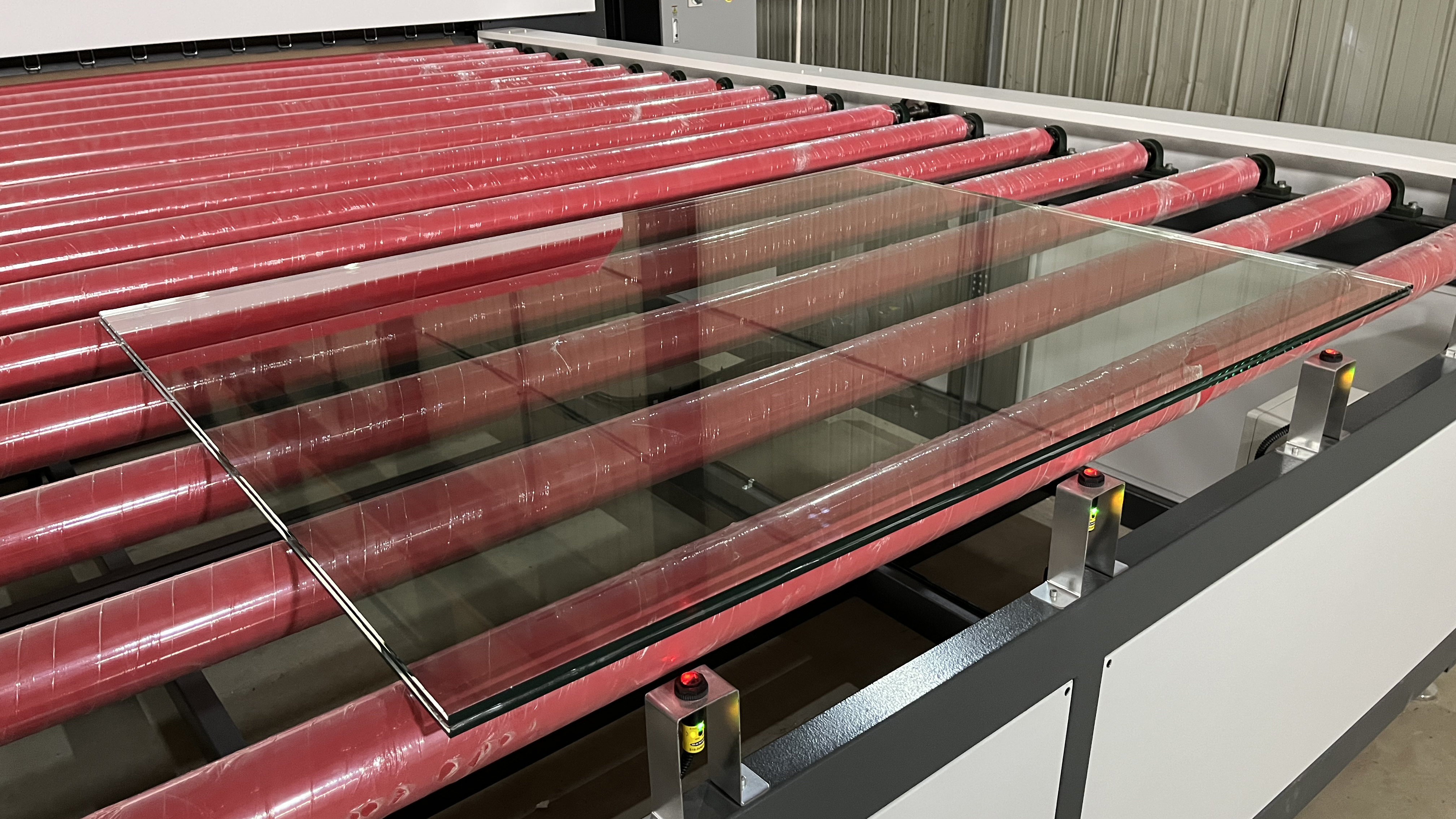
Laminated glass is made from two or more sheets of heavy pressed, reflective glass with an inner pane of strengthened clear glass. This makes it ideal for windows, as the combinations of coatings and layers provide increased insulation and emissions protection. It is also possible to use different glass combinations to meet individual requirements. Each outer pane of glass must meet specific safety requirements, ensuring that the window is secure, and then these panes are laminated together to meet the specified safety standards. Laminated glass provides a level of protection which isn't available when using tempered or standard float glasses alone; it combines strength with comfort and protection.
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass, it consists of two or more layers of glass held together by an interlayer. The interlayer is a strong plastic material which holds the glass layers together when subjected to impact or pressure. When the laminated window glass is broken, it does not shatter into small pieces and instead forms small fragments which are held in place by the interlayer; this makes it ideal for use in areas where safety is paramount. For structural projects, specifying a specifier should always be done. This ensures that your windows meet all necessary requirements and are suitable for their purpose. There are more standard sizes available than non-standard sizes and many laminated glasses have a list of safety specifications as well as size and thickness options to choose from.